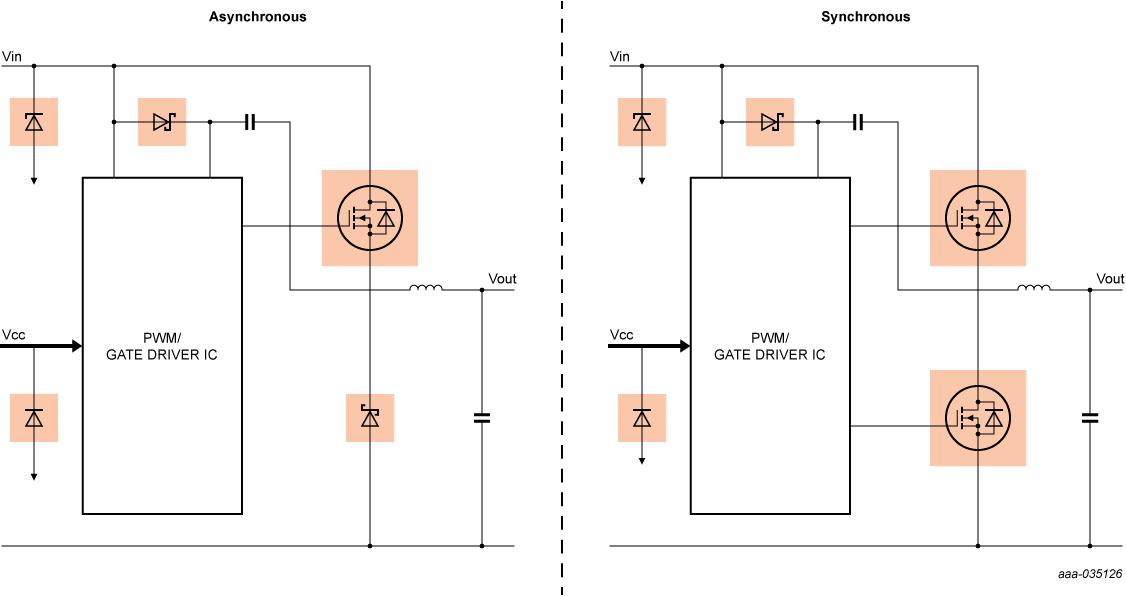
Block diagram
S2 can be replaced by one Schottky diode to be in asynchronous mode.
Highlighted components are Nexperia focus products
Products - Signal conditioning
Design challenges
- Point of load non-isolated DC/DC buck converter circuit
- Step-down of voltage while stepping up current
- Easily switch from asynchronous to synchronous buck converter circuit depending on choice of low-side diode or MOSFET
- Economical, two-MOSFET design - low QG(tot) and low FOM for best efficiency
- Lower switch losses improve thermal behaviour
- LFPAK and CFP (both clip-bond package) allow a high-efficiency DCDC converter solutions, while reducing costs (less heating to dissipate)
- Possibility to go to higher switching frequency (FSW), which leads to smaller inductances and smaller capacitors
- Best thermal performance thanks to clip-bonding package
MOSFET and GaN FET Handbook
Drawing on over 20 years’ of experience, the MOSFET and GaN FET Application Handbook: A Power Design Engineer’s Guide brings together a comprehensive set of learning and reference materials relating to the use of MOSFETs and GaN FETs in real world systems.
Let us help you with product and design questions
Contact our technical support desk for your technical questions.